Plasma systems
What is Parylene
Chemical
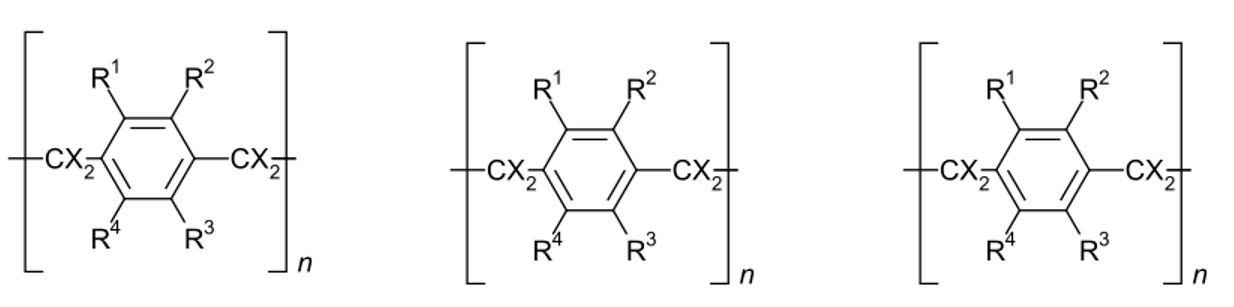
PARYLENE is the GENERIC NAME for a series of polymers based on p-Xylylene
POLY (PARA-XYLYLENE)
General chemical structure

Substantial
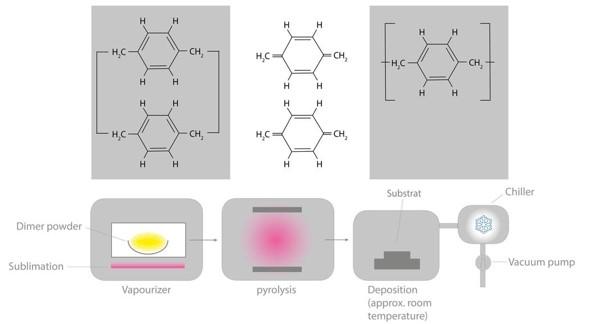
Raw material of parylene is available in the form of a powder

After a chemical vapor deposition process parylene composes a poylmer film with extraordinary properties.
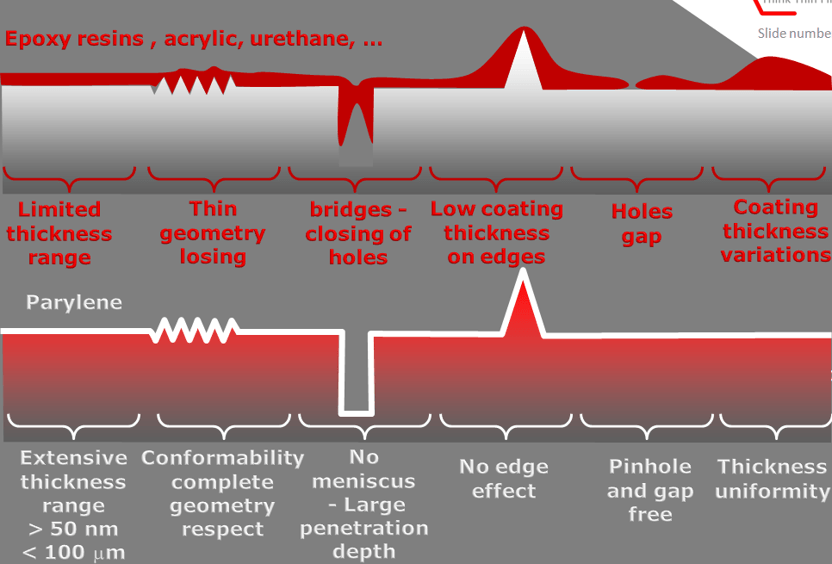
Substantial adventages of the parylene technology
✔ Optical transparent

Applications of parylene
electronics / sensor technology
- In places, where electronic components are exposed to corrosive media, to moisture or high radiation
- For electronics of high-quality devices with high safety significance
- For significant lifetime extension of LED's, sensors,..
medical / pharmaceutical
- Parylene are resistant to all body fluids
- Minimal abrasion (better than PTFE) and very good sliding properties allow easy insertion of stents, needles and catheters
- US FDA certification for direct food contact
- Certified according to ISO 10993 - Biological properties and biocompatibility of medical devices
- Parylene are resistant to all common sterilization processes

aviation / aerospace
- According to failures of systems, very high values and human lives are at the risk to be lost. Therefore, the effort for the best possible protection of the vital components, is worthy in any case.
- Certification to the highest aerospace and military standards (US MIL-I-46058C, UL listed, NBC AR 70 / AFR 80-38 / Navinst 3400.2) provides safety even in other fields with high stress and safety relevance.
- Protection against high-energy radiation with Parylene HT at low film thickness (requirements of a low weight/volume ratio).

aviation / aerospace
- Coating of gaskets (O-rings) for easier assembly (low coefficient of friction), or to increase the lifetime.
- Protective and self-cleaning (hydrophobic) coating of optical components.
- Elastomers are often sensitive to ozone, hydrocarbons, UV. Parylene offer a long-term protection.
- Barrier coating on containers, vials or tubes.

Manufacturing of parylene coatings by chemical vapor deposition
Dimer →→
Monomer →→
Polymer
Parylene coating can be carried out on about all materials and multimaterial assemblies
The only restriction are:
Vapour pressure of each material or compound constituting the part will have to be sufficiently low to avoid its vaporization or sublimation at room temperature (max. 40°C ) during vacuum process.
→ Dimensions are limited by the deposition chamber volume
→ Chamber size P300: Height: 720 mm Ø: 700 mm
→ Remark: very large chamber can be realized
Adhesion performances is a combination of:
Mechanical adhesion:
Roughness – Porosity Complex geometry
+
Crevice penetration of parylene
Chemical adhesion:
To improve the chemical adhesion specific adhesion promoter(s) can be used
+
Monomer reactivity
→ → Surface preparation is a key factor affecting the final success of parylene treatment.
Coating methods
Parts are arranged on carrousel, which will turn slowly in the chamber during the process. Laid out on trays or hanged up on support device
For brittle parts and devices Contacts points not coated. (if masking: contact points correspond to masked areas).
Tumbling process:
Parts are coated in bulk in a closed barrel turning slowly avoiding parts conjoining with coating.
For quite small parts and large quantity
- complete encapsulation
- “Low damaging material” like ferrites, elastomeric parts, … Hammering, loss of transparency: coating more or less milky.



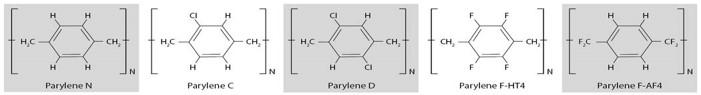
Parylene N
Basic model, made up only of the atoms of hydrogen and carbon. But not the most common type. Extraordinary good penetration in crevices and holes. Optimum dielectric properties and dielectric strength and therefore preferred for the coating of electronic components and assemblies. Lowest friction coefficient, popular for application of catheters. FDA conform
Parylene C
The most utilized product with excellent barrier properties. High moisture protection and supported by the good hydrophobic properties. High elasticity, therefore suitable coating for plastics and rubbers. Low coefficient of friction. High deposition rate (up to 10 microns / h). FDA conform
Parylene D
Used for a long time, due to its elevated temperature stability. But it is also very hydrophobic. Used for protecting electronic components in the aerospace industry.
Parylene F-VT4
Since, it withstands thermally even higher loads than Parylene D, it displaces this increasingly in applications with higher temperature load. It is much cheaper than Parylene HT.
Parylene F-AF4
By far the highest temperature stability of all Parylene types. In addition, this type is very insensitive to aggressive radiation exposure, especially to UV. The most expensive version, therefore only used when these special properties are necessarily required.
→ → Diener electronic will support you to find the right parylene type for your product
Adventages of parylene compared to other coatings